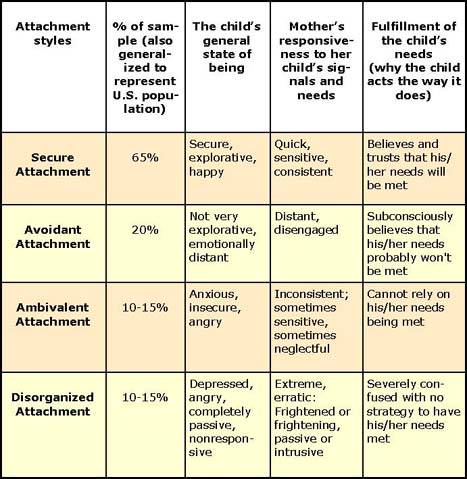
Characteristics of Secure Attachment Observed. About ____ in 10 infants display a secure attachment style.
 The Four Infant Attachment Styles Spot On
The Four Infant Attachment Styles Spot On
While the first component refers to the liking of infants the second and third components entail the wanting of an infant.

Infants who display secure attachment. Insecure and secure attachment refer to specific attachment behavior patterns that the infant shows typically when being under some form of stress. Research indicates that 23 of the population display an avoidant attachment pattern. Within psychology attachment behavior of this stage is characterized by.
An insecure attachment bond one that does not meet a childs need for security calm and understanding can hinder a childs brain development for optimal organization. According to Cassidy and Berlin ambivalent attachment is relatively uncommon with only 7 to 15 percent of infants in the United States displaying this attachment style. Attachment theory Bowlby 1969 1973 1980 is rooted in the ethological notion that a newborn child is biologically programmed to seek proximity with caregivers and this proximity-seeking behavior is naturally selected.
When this secure attachment is formed early in life the child sees their parent as a firm base from which to explore the world. A child with a secure pattern of attachment will explore a room while the parent is present. One he calls autoregulation which is self-soothing or using his own mind and body to manage feelings.
Children who have a secure attachment with their caregiver often turn to them for comfort when frightened. Asked Apr 11 2016 in Psychology by Stigma. When the infant is between 0-8 weeks of age the stage for developing secure attachment is being set.
You will notice that this gives the infant the confidence to explore and try new things. If the parent leaves the room the child will show signs of missing the parent during the. It can also restrain.
The infant knows that the caregiver is dependable which creates a secure base for the child to then explore the world. The central theme of attachment theory is that primary caregivers who are available and responsive to an infants needs allow the child to develop a sense of security. In a review of ambivalent attachment literature Cassidy and Berlin also found that observational research consistently links ambivalent insecure attachment to low maternal availability.
They often display postive emotions and prefer their caregiver to strangers. When an infant shares a secure attachment with their caregiver they will feel safe and secure whenever this adult is around them. The second is interactive regulation which is going to other people to help up- or down-regulate feelings.
They are honest supportive and comfortable with sharing their feelings. Informed by leaders in the new field of infant mental health this HelpGuide video demonstrates what a secure attachment bond looks like from the perspective of the infant as well as the parent. Random intercepts multilevel models with emotion nested within participants revealed a significant interaction between secure attachment state and emotion on both liking and representational response.
Children who experienced secure childhood attachment generally move on to successful intimate relationships as adults. If this adult leaves them for example walks out of the room they may protest by crying or trying to follow them. During this pre-attachment period the mother will warm up the emotional bond with her sensitive and consistent responses.
These patterns have been largely shaped by the mothers sensitive responsiveness secure attachment or lack or inconsistency of responsiveness insecure attachment. Additionally the video explains why a loving parent may not be able to create a secure attachment bond or why an infant may not be able to participate in the two-way emotional exchange that creates this bond. Typical Avoidant Attachment presentations.
Research on Bowlbys theory of attachment showed that infants placed in an unfamiliar situation and separated from their parents will generally react in one of three ways upon reunion with the parents. In the Strange Situation a securely attached infant for example may be upset when the caregiver leaves but may be happy to see the caregiver return recovering quickly from any distress. A secure attachment in childhood the most common type usually produces adults with higher self-esteem and self-confidence who form healthy lasting relationships.
Schore explains that in a secure attachment the baby learns to self-regulate in two ways. These infants showed distress upon separation but sought comfort and were easily comforted when the parents returned. A pattern of attachment in which infants or young children have a high-quality relatively unambivalent relationship with their attachment figure.
A Welcome to Sciemce where you can ask questions and receive answers from other members of the community. Children who display avoidant attachment are at least able to work out an organised way of achieving some access to their attachment figure. Answered Apr 11 2016 by BlaqueBeauty.