Breastmilk contains all of the essential vitamins necessary for the babys survival for the first six months of their life including fat carbohydrates proteins vitamins minerals and water According to NBCI There are two hormones that directly affect breastfeeding. Breastfeeding hormones 6 months postpartum.
 Concentration Changes In Human Milk Hormones From 1 To 3 Months Post Partum Download Scientific Diagram
Concentration Changes In Human Milk Hormones From 1 To 3 Months Post Partum Download Scientific Diagram
I had my hormone levels checked 6 weeks postpartum and my progesterone and estrogen levels were very low.

6 months postpartum hormones. Delayed postpartum depression can strike a woman 18 months after birth or later depending on hormonal changes within the mothers body. She also added that The changes you should look for closely are not wanting to shower or focus on hygiene being afraid of leaving your baby with someone else not being able to sleep fully due to continually checking on baby and lack of desire for common tasks like eating drinking being around. I NEVER get cross or annoyed with my daughtermy poor husband usually cops.
7 - 2 weeks. 3 - Day 4. 2 - Day 2.
14 - 6 months. Learn about some of the causes of the delayed postpartum depression its symptoms and what you can do to get help. A number of other hormones such as estrogen.
An Interview With Heng Ou By Casie Leigh Lukes. Postpartum Hormones at 6 Months The biggest change that occurs to your hormones after six months postpartum is the decrease of the hormone prolactin which is the milk-making hormone. 13 - 4 months.
She added that post-birth hormones and postpartum hormones continue to fade after 6 months. The postpartum or postnatal period begins immediately after childbirth as the mothers body including hormone levels and uterus size returns to a non-pregnant state. I get stressed feeling easily and foggy headed.
15 - 9 months. Its normal for this to last up to 6-12 months postpartum but should taper off after noticing a peak around 4-6 months. Personally I thought the regrowth with the shorty hairs was worth than the shed.
9 - 4 weeks. In fact postpartum depression can begin as early as right before giving birth and as far along as 12 months after having your baby. I hope you are all doing really wellI have been doing so well with my adorable girl and still am.
16 - 1 year. 12 - 3 months. Just a few weeks ago Ive been feeling symptoms of pregnancy that are similar to how I felt while pregnant with her.
The terms puerperium puerperal period or immediate postpartum period are commonly used to refer to the first six weeks following childbirth. 11 - 2 months. 10 - 6 weeks.
You could try red raspberry extract a bioflavonoid and hormone-rich ingredient that helps to strengthen vessels. I am 5 months postpartum and suffering from anxiety and a little bit of depression. Back 1 - Day 1.
The first six weeks after giving birth known as the postpartum period is an intense time and requires all sorts of care for you and your baby. This means that you are likely still experiencing postpartum hormonal changes - even months after your babys birth. Emollients like olive oil or shea butter can help to keep the skin around the vessels soft.
The Essential Art of Nourishing the New Mother talks to us about ways to honor the postpartum season. I havent been sleeping well and have been very anxious during the day. When hormone levels drop after birth you lose some luscious locksand start a new phase of growth.
5 - Day 7. Ever since last week my anxiety and emotional outbursts have been on high. Most of them feel shame that six nine or even 12 months after giving birth theyre still carrying extra weight.
High hormone levels during pregnancy cause you to grow more hair over the nine months. - Hormones - Nourishing Care for the Postpartum Mom. Did anyone get crazy mood swings 6 months postpartum.
I used bioidentical progesterone cream prior to pregnancy with great results. Check out its symptoms and possible ways of treatment. By month 3 postpartum I was 2 lbs away from my pre-pregnancy weight.
However my mood swings are terrible. Just dont feel myself. Did anyone experience an extreme rush of hormones around the 6 month mark.
Most women notice an improvement four to six months post-birth but some will require a dermatologists help to lessen their appearance. My body looked a lot different though I was much softer had lost a lot of muscle. Signs of postpartum depression Postpartum hormonal shifts can leave many new parents feeling down and not like their usual selves.
I feel like I may be going a bit bonkers here. 6 month postpartum hormones. Heng Ou the author of The First Forty Days.
Being informed of the process of postpartum recovery will help you to appreciate the phenomenal transformation your body is undergoing. All my hpts have been negative and I have yet to have a period so no idea of what my cycle is like. Cue the hormonal mayhem.
8 - 3 weeks. During this time your body will experience a. Hi everyone I have a 65 month old daughter that I am breastfeeding.
For 6 weeks after that I was incredibly consistent working out 4-5 times a week but for only 20-30 mins at a time walking for 45mins 3-4 times a week. 4 - Day 5. 6 - Day 10.
Hi LadiesI used to read a lot and sometimes post when I was pregnant but havent been on for quite a while. Postpartum thyroiditis can last up to 18 months so its a good idea to consult with your health care provider if you spot any of these symptoms. As a nutritionist Ive talked to hundreds of women specifically about the issue of postpartum hormones and weight loss.
After pregnancy postpartum hormones go down to menopausal levels. The World Health Organization WHO describes the postnatal period as the most. What to expect at your six-week postpartum check-up How to deal with postpartum anxiety.
Little is known about the mechanisms that regulate the growth of the fetus and placenta during protein malnutrition. Eight weeks into your pregnancy or six weeks after conception your babys lower limb buds take on the shape of paddles.
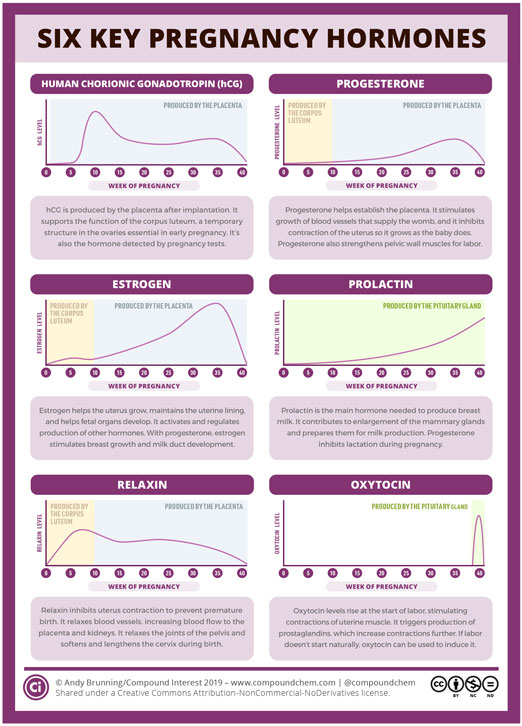 Six Key Pregnancy Hormones American Scientist
Six Key Pregnancy Hormones American Scientist
Glucocorticoids are essential for fetal development Fetus own cortisol and cortisone are the most important hormones regulating fetal tissue maturation.

Fetal development hormones. After ovulation the opened ruptured follicle develops into a structure called the corpus luteum. Fetal development six weeks after conception By the end of the eighth week of pregnancy six weeks after conception your baby might be about 12 inch 11 to 14 millimeters long. These steroids belong to a family of hormones called the glucocorticoids which are known to be associated with the regulation of stress.
Other hormones such as the steroid hormones corticosterone and cortisol are important for fetal development during pregnancy. Hormones play a central role in regulating fetal growth and development. This family of hormones is also known as the steroid hormones or the stress hormones.
The human fetus is dependent upon endocrine development for hormones which support normal development. They act as maturational and nutritional signals in utero and control tissue development and differentiation according to the prevailing environmental conditions in the fetus. Cortisol levels increase continuously during the third trimester and are dramatically elevated in face of anxiety and in chronic stressful conditions.
The other luteinizing hormone LH causes growth and secretion of the testosterone-secreting cells of the male and has an action in controlling the menstrual cycle in the female. Hormone exposure and fetal sex development While your babys chromosomes determine his or her sex medications containing hormones can affect fetal sex development in particular spironolactone a high blood pressure medication that reduces testosterone. This secretes releases the hormones progesterone and estrogen.
Thyroid hormones are intricately involved in the developing fetal brain. The corpus luteum is a temporary structure in the ovaries which produces other key hormones during early pregnancy. One follicle-stimulating hormone FSH causes growth of the main portions of the ovary in the female and the sperm-producing cells in the testis of the male.
Around week 16 GA week 18 the fetal thyroid becomes active enough to support the fetal requirements for neural development. Disruption of the IGF1 IGF2 or IGF1R gene retards fetal growth whereas disruption of IGF2R. Pancreatic Hormones maternal diabetes can affect fetal pancreas development increase in fetal islet beta cells.
The pituitary secretes two other hormones concerned in development. It is known that the placental size and levels of circulating placental hormones such as human chorionic gonadotrophins hCG human placental lactogen hPL and estrogens are affected by the nutritional status of the mother. At 20 weeks the fetus is able to implement feedback mechanisms for the production of thyroid hormones.
The hormonal theory of sexuality holds that just as exposure to certain hormones plays a role in fetal sex differentiation such exposure also influences the sexual orientation that emerges later in the adult. Peripheral endocrine glands thyroid pancreas adrenals gonads form early in the second month from epithelialmesenchye interactions and differentiate into the third month. In the first trimester the developing fetus is initially dependent upon maternal thyroid hormone crossing the placental barrier.
The insulin-like growth factor IGF system and IGF-I and IGF-II in particular plays a critical role in fetal and placental growth throughout gestation. Critical amounts of maternal T3 and T4 must be transported across the placenta to the fetus to ensure the correct development of the brain throughout. Several aspects of placental function are critical for human fetal growth and development including adequate trophoblast invasion an increase in uteroplacental blood flow during gestation transport of nutrients such as glucose and amino acids from mother to fetus and the production and transfer of growth-regulating hormones.
During fetal development T 4 is the major thyroid hormone being produced while triiodothyronine T 3 and its inactive derivative reverse T 3 are not detected until the third trimester. Gonadal Hormones testosterone - required during fetal development for external genital development and internal genital tract in male. The fetal central nervous system is sensitive to the maternal thyroid status.
Estrogens - secreted inactive precursor converted to active form by placenta. Its produced by the placenta after implantation and supports the function of the corpus luteum. The adenohypophysis constitutes 80 of the pituitary gland and houses specialized hormone-producing cells that synthesize and secrete several hormones including but not limited to growth hormone GH thyroid-stimulating hormone TSH follicle-stimulating hormone FSH luteinizing hormone LH prolactin and adrenocorticotropic hormone ACTH.
Human chorionic gonadotropin hCG hCG is an important hormone in early pregnancy. The progesterone helps prepare the endometrium lining of the uterus. Another important family of hormones to the fetuss development are the glucocorticoids like cortisol and corticosterone.
This lining is the place where a fertilized egg settles to develop. Prenatal hormones may be seen as the primary determinant of adult sexual orientation or a co-factor with genes biological factors andor environmental and social conditions.