Within the participating American students Asians performed the best. Adding to the literature base to include evidence from non-Western nations such as China serves to extend and deepen knowledge of parent-adolescent relationship processes.
 Over Parenting Is Harmful For Children
Over Parenting Is Harmful For Children
Research from 2009 shows that parents who recall physical abuse in their own childhoods are 5 times more likely to be physically abusive parents and 14 times more.

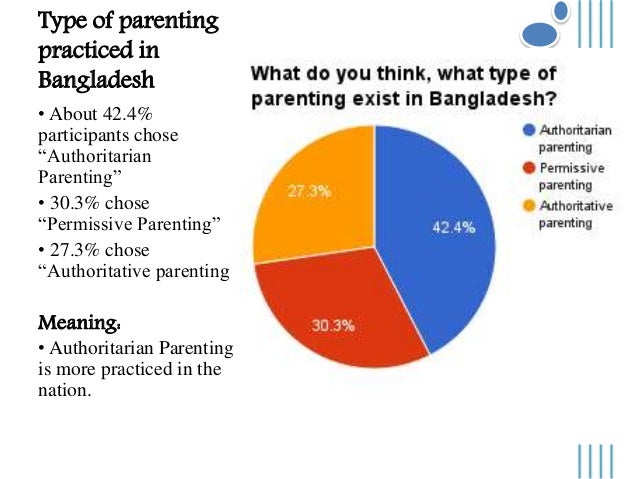
Authoritarian parenting statistics. Have a look at the authoritative parenting statistics. It insists on unquestioning obedience and enforces good behavior through threats shaming and other punishments. Parents with an authoritarian style have very high expectations of their children yet provide very little in the way of feedback and nurturing.
Clearly more than 80 of children raised by authoritative parents exhibited positive behavior along with a responsible attitude during the study. May be physically abusive. The pros and cons of authoritarian parenting show that it can be beneficial but requires a certain level of flexibility.
About six-in-ten moms 58 and dads 57 say this and an additional 35 and 37 respectively say being a parent is very important to their overall identity. It focuses on obedience discipline and control and provides little nurturance to the child. Some researchers have found that even in Asia authoritarian parenting is linked to worse academic performance while authoritative parenting produces better academic outcomes 17.
This style is also called autocratic parenting. By building rules that allow for variable options if that line in the sand gets crossed more independence and self-reliance can be achieved to offset the potential negatives of this parenting style. Authoritarian parenting is a parenting style characterized by high demands and low responsiveness.
97 permissive parents 14 authoritarian and 98 authoritative parents when motivating open communication. Calzada Barajas-Gonzalez Huang. For example while some studies found the use of authoritarian parenting in the Chinese American population was associated with the best academic outcomes 23 others found the authoritative parenting to be the best in predicting school performance 24.
The authoritarian stance that people often take is reflected in the parenting style of those who criticize these programs yet their own behaviors as a parent is what creates the need for them. Mothers and fathers are equally likely to say that being a parent is extremely important to their overall identity. We know of only one relevant published study of parenting styles and parentadolescent relationships which found that authoritative mothers exhibited the highest levels and authoritarian mothers the lowest levels of mother-adolescent cohesion Zhang et al 2017.
Do you want to know the ways to be an authoritative parent. That same study by the National Institutes of Health also found that children of authoritarian parents also had higher than average body mass index. How To Be An Authoritative Parent.
It is one of the three parenting styles originally propounded by. As defined by psychologists its also a style associated with less parental warmth and responsiveness Baumrind 1991. In a recent international meta-analysis of 428 published studies researchers found that authoritative parenting is associated with at least one positive outcome in every region of the world.
Authoritarian parents are the least likely to have children who hit the ground running equipped with the tools that they need to succeed. In this way the short term behavioral gain of obedience is heavily outweighed by the long term psychological damage. Authoritarian parenting is associated with many externalizing and internalizing problems in both girls and boys Akhtar Malik.
In at least one key area gender does not make a difference. Hartman et al 2014. What the data shows is pretty clear.
A recent PISA international standardized test kids in China ranked on top in all three fields reading math and science and by a wide margin. One Chinese study on second graders shows that children with authoritarian parents are not only worse in academic achievement but are also rated as poorer in social competence by their teachers. When feedback does occur it is often negative.
The authoritarian parenting style is about being strict and stern. Research has shown that children of authoritarian families are more prone to suffering from low self esteem and low self-worth than children coming from authoritative or permissive parents. Authoritarian parenting is characterized by high demandingness expectations and low responsiveness meeting the childs wants and interests.
Clark Dahl en. Authoritarian parenting statistics 20. Across cultures authoritative parenting is consistently linked with better child outcomes.
Braza et al 2015. Authoritative parenting is one of four parenting styles based on the research and work of developmental psychologist Diana Baumrind. This is attributed to their parents authoritarian parenting style.
Both types of bullying were significantly related to self-reported authoritarian parenting therein suggesting that this parenting style is more prevalent in the households of bullying. Mistakes tend to be punished harshly. In Canada almost 25 of children are raised using overly permissive style of parenting.
Gracia Garcia and Lila in 2008 developed a parenting style index to assign the parents to four categories based on their parenting style namely authoritative authoritarian neglectful and indulgent Gracia Garcia Lila 2008. Researchers have identified four types of parenting styles.
 Parenting Styles An Evidence Based Cross Cultural Guide
Parenting Styles An Evidence Based Cross Cultural Guide
A common way of addressing these complexities is to organize parenting behaviors into four distinct parenting styles.
/1095045-article-types-of-parenting-styles-5a7cb6aaa18d9e00362ef5eb.png)
Four parenting styles statistics. The four types of parenting styles are. The four Baumrind parenting styles have distinct names and characteristics. Each parenting style varies in at least four areas.
Many of the behavior statistics come from individual interviews which could skew the statistics of behavior as authoritarian kids are generally more fearful of authoritarian figures. There are four different types of parenting styles that are commonly identified by an expert by the name of Diana Baumrind in the parenting field. Later research by Maccoby and Martin suggested adding a fourth parenting style.
These concerns also have led to new more granular. Authoritative authoritarian and permissive. A persons style of parenting in no way speaks about the level of love they have for their children.
Parenting Styles describe the way parents react and respond to their children. When it comes to parenting there are three basic styles. While the authoritarian is demanding for compliance the permissive parent is more willing to let the child make their own decisions and let natural.
Studies suggest that kids from authoritarian households have less moral reasoning and self-regulation than kids exposed to other parenting styles. When researchers want to identify an individuals parenting style they often use a kind of rubric or questionnaire. Authoritarian or Disciplinarian Permissive or Indulgent Neglectful or Uninvolved.
23 Interesting Permissive Parenting Statistics. The four-fold typology of parenting is usually based on crossing the often used dimensions of responsiveness and demandingness characterizing authoritative styles as parents who are both responsive and demanding authoritarian styles as parents who are less responsive but highly demanding permissive or indulgent styles as parents who provide. Teens with authoritarian parents are less likely to feel socially accepted by their peers than any other parenting group.
These are Authoritarian permissive authoritative and uninvolved. Research from 2009 shows that parents who recall physical abuse in their own childhoods are 5 times more likely to be physically abusive parents and 14 times more. May be physically abusive.
In some cultures kids dont start school until the age of 7 have minimal homework and take long breaks during school. For example they may present a parent with a series of statements and ask the parent to rate his or her agreement on a four-point scale 1 almost never true 4 almost always true. Children raised with this parenting style tend to be impulsive rebellious aimless domineering aggressive and low in self-reliance self-control and achievement.
Thats not biblical discipline. Authoritarian or Disciplinarian Permissive or Indulgent Uninvolved Authoritative These Baumrind parenting styles are United States-centric and it is not clear how well these styles describe parents cross-culturally. Parenting looks different in every culture around the world.
152 240 of total sample authoritarian. And 177 280 indulgent. Discipline style communication nurturance and expectations.
Its important to ensure your parenting style is supporting healthy growth and development because the way you interact with your child and how you discipline her will influence her for the rest of her life. Here you will find information about the four basic parenting styles. Instrument is assessing parenting style independent of parenting practices.
These dimensions include disciplinary strategies warmth and nurturing communication styles and expectations of maturity and control. Terms of global consistent and stable parenting styles. Regarding descriptives the following frequencies were found for the four parenting styles.
Based on these dimensions Baumrind suggested that the majority of parents display one of three different parenting styles. These styles are known as authoritarian parenting permissive parenting neglectful parenting and authoritative parenting. First its important to understand how your parenting style may be contributing to the problem especially in a culture that has made discipline a dirty word.
Authoritarian permissive uninvolved and authoritative Maccoby Martin 1983. These four parenting styles are sometimes called the Baumrind parenting styles or Maccoby and Martin parenting styles. Generally there are four different types of parenting styles.
To speak of a parent disciplining a child today evokes images of unreasonable anger and brutal beatings. May 23 2017 by Brandon Gaille. Authoritative parenting who encourage kids to be responsible to think for themselves and to consider the reasons for rules Authoritarian parenting who expect their orders to be obeyed without question and who rely on punishment--or the threat of punishment--to control their kids.
However studies examining variations along different parenting dimensions now predominate due to concerns about whether styles accurately capture contextual varia-tions and have the same meaning in different groups.
But by the turn of the millennium the number of toddlers who were potty trained at age twothat is 6 months later than those kids in the 1957 statisticwas only 4 percent. The age for potty training is rising.
Potty Training Not A One Size Fits All Concept Kidsdirectory
However some children wont be trained until after they are 3 and a half years old.
Potty training age statistics. But by the 1980s approximately 70 of kids hadnt even started potty training by that age. The perfect age to begin potty training is different for every child. Virtually no one would think of an infant twelve weeks old as ready to begin shedding the diapers.
During the 1950s the average age for a child to be potty trained was between 15 and 18 months but now it is age three-and-a-half. In the 1940s the average age for potty training was 18 months. Since training at a young age and helping children be independent can help them in the later stages.
In general girls tend to complete potty training about three months earlier than boys. However others might not be ready until theyre 3 years old. Quick Facts About Potty Training.
In 1957 92 percent of children in the United States were toilet trained by 18 months of age. By the age of three 9 out of 10 children are dry most days. By the age of four most children are reliably dry.
2 Its okay to trade candy for poop. 92 of children in 1957 were toilet trained by 18 months NY Times 1999 The current average age of potty training completion in the US is 35 months for girls 39 months for boys Ambulatory Pediatrics Journal 2001. Author of The No-Cry Potty Training Solution.
In 1947 approximately 60 of children had finished toilet training by the time they were 18 months old Martin et al 1984. English is used when calling us. So try not to worry or compete with others wait to start toilet training at the right time for your child.
Back in the 1940s the average age for a kid to be potty trained was 18 months. And they wont have age-related difficulties since the older they are the more difficulty they tend to face during learning. Many children show signs of being ready for potty training between ages 18 and 24 months.
The average age of potty-training rises. Your childs best starting age could be anywhere from eighteen to thirty-two months. Not only has the average age risen in the United States but its risen in Brazil China and Switzerland as well.
The first step is to know the facts. In fact I would wager some people would think parents are committing some sort of abuse by starting the training that early. Averages today according to a 2001 study by Schum show baby boys in the United States give up.
703 369-2100 or 703 491-2222. In 1974 about 60 were trained later at 33 months. Potty training can be natural easy and peaceful.
But rushing toilet training is counter-productive and its worth bearing in mind that. The average child wasnt finished training until he or she was between 24 and 27 months old Seim 1989. One reason for this is the widespread availability and convenience of disposable diapers.
Autism and potty training age is an important factor. Children now become potty trained at an average of three years instead of just a few months over two years. The average age of potty training falls somewhere around 27 months.
According to American Family Physician 40 to 60 percent of children are completely potty trained by 36 months of age. Lets take a quick look at some eye-opening statistics from this chart. And even from that point it can take several months.
Most children start working on this skill between 18 months and 3 years of age. They found that in the US in 1947 60 of children were toilet trained at 18 months. In the US children begin potty training somewhere between 18 months and three years.
By 1980 the average toilet trained age varied from 25 to. Potty training success hinges on physical developmental and behavioral milestones not age. Recent American epidemiologic studies note that approximately 25 of 2-year-old children are daytime potty trained 85 by 30 months of age and 98 by 3 years of age.
A research conducted in the United States in 2001 by Schum revealed that the average age for potty-trained girls was 35 months while that of boys was 39 months. The timeline for your child will depend on their. WebMD says that most children arent ready to start potty training until they are between 22 and 30 months of age.
It is joyful and provides an outlet for anxiety and stress. Play helps children grow strong and healthy.
 Copy Of Digital Game Based Learning By Kathryn Procope
Copy Of Digital Game Based Learning By Kathryn Procope
Giving students occasions to learn through play not only fosters creative thinking problem solving independence and perseverance but also addresses teenagers developmental needs for greater.

Learning through play statistics. Key ways that young children learn include playing being with other people being active exploring and new experiences talking to themselves communication with others meeting physical and. Learning Through Play in the Early Years. Their classmates and teachers through play.
With a mission to spark childrens learning through play Minnesota Childrens Museum provides hands-on learning experiences to more than 400000 visitors each year in Minnesota as well as millions of children around the country through the leading traveling exhibit program for childrens museum. According to the book From Play to Practice. When learning is perceived to be arduous our ability to stay focused may feel like a limited resource that is drained over time Inzlicht et al 2014.
Why should people learn statistics. Our play-based approach crosses all areas of early childhood learning including emotional social and physical development literacy numeracy problem solving negotiation and collaboration. Evolves spontaneously rather than giving kids a script to follow.
Learning Statistics through Playing Cards. Play contributes to language acquisi on early literacy conceptual learning problem solving large and small motor skills and crea vity. It also counteracts obesity issues facing many children today.
Play is more than meets the eye. Play helps your children grow emotionally. Data suggest administrators greater support for outdoor play and learning than previously identified.
G Burriss L. The methodology and suggested progression in this document is appropriate for the proposed Foundation Stage as recommended. Individuals take an active role in the learning environment They are engaged Information is meaningful Learners interact in a social context This means that children learn well when they are mentally active engaged social.
Kathryn Hirsh-Pasek a well-known child development expert in the Department of Psychology at Temple University and a Senior Fellow at the Brookings Institution argues that humans learn best when at least one of these four pillars are present. Experiences with other people objects and events. Play is recognised as so important to their well-being and development that the right to play is set down in the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child 1989 and play is a.
A play-based program builds on this motivation using play as a context for learning. This is in contrast with activities that we perform as duties. Through play children can develop social and cognitive skills mature emotionally and gain the self-confidence required to engage in new experiences and environments.
Learning through play is a term used in education and psychology to describe how a child can learn to make sense of the world around them. First of all the popular press and other media are full of statistics particularly percentages and differences between percentages which are the primary focus of this book and an understanding. Thus anything learned during play is knowledge gained without the perception of hard work.
Furthermore there has been many studies stating that play increases creativity in children teaches them social skills and so on. As they explore and learn children are naturally drawn to play. This booklet has been compiled by the Early Years Interboard panel in response to requests by practitioners in Early Years settings for guidelines on provision and progression in play.
These findings are dis cussed as an opening dialogue between administration and teachers to plan for childrens quality outdoor experiences. Play is self-motivated and fun. Children are most recep ve to learning during play and explora on and are generally.
Through our observations assessment and professional judgementwegainvaluableinsightsintohoweachonelearnsbest. Connecting Teachers Play to Childrens Learning meaningful play has five characteristics. Children come to pre-school already as skilled learners.
Play is expected to be part of the learning practice in Primary 1 and Primary 2 through CfE and this is perhaps an area where qualifications for Pupil Support Assistants provide a bridge across the active learning curriculum and playwork especially where options to cover playwork training are taken up by assistants. Gives the child a choice about what he or she wants to do. Learning is broad interconnected and dynamic 8 Children are born to learn through play 12 Characteristics of playful learning experiences 16 Joyful 18 Meaningful 20 Actively engaging 22 Iterative 24 Socially interactive 26 Future directions and unanswered questions 28.
Outdoor play and learning. Play is simple and complex. Progression in play reflects the observation and assessment of childrens knowledge skills and attitudes in order to provide developmentally appropriate experiences.
Feels fun and enjoyable for the child. Literature search we found that learn through play is a method of learning where children could make sense of their environment and learn through the act of playing. In this context children can explore experiment discover and solve problems in imaginative and playful ways.
A key element to consider is learning through play or playful learning which is central to quality early childhood pedagogy and education3 This brief will help pre-primary stakeholders advocate for making play-based or playful learning a central aspect of expanding and strengthening the pre-primary sub-sector.