This is evidenced first by the infants attempts to be close to the caregiver then by the infants readiness to explore. Secure and insecure attachment Individuals and Society MCAT Khan Academy.

Secure Attachment Group B Bowlby 1988 described secure attachment as the capacity to connect well and securely in relationships with others while also having the capacity for autonomous action as situationally appropriate.
Secure attachment vs insecure attachment. In the first year of life we are sponges absorbing everything in our environment as well as the interaction with and between our caretakers. In a secure relationship the child seeks comfort from her caregiver and prefers her over strangers. If it were a child of avoidant insecure attachment they would have ignored the exiting and return of their mother.
Also secure attachment helps the child to develop self regulation toward stress which helps in conflict resolution such as preventing potential tantrums. As the infant grows so does the bond of trust with the primary caregiver. Over the past 60 years there has been a lot of research about attachment in early childhood.
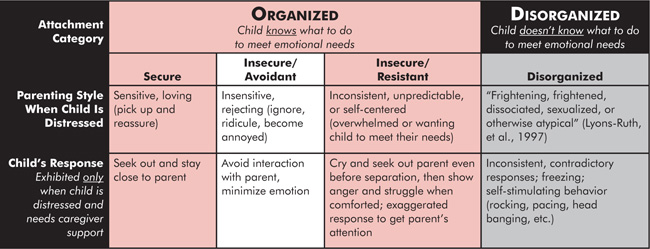
Ainsworth 1970 identified three main attachment styles secure type B insecure avoidant type A and insecure ambivalentresistant type C. Find Out How To Identify Yours And How It Affects Your Relationships. If a youngster is not provided this consistent loving care insecure attachments form.
Secure Attachment To really understand the importance of attachment we must have some basic understanding the development of the nervous system and brain. Attachment Types Trauma. If playback doesnt begin shortly try restarting your.
Children who have an ambivalent-resistant attachment express anger when their mother returns to them and they are not easily soothed. Children who are insecurely attached have learned that adults are not reliable and do not trust easily. A bond can be classified as an insecure attachment bond or a secure attachment bond.
Infants whose experiences with a caregiver are negative or unpredictable are more likely to develop an insecure attachment. When a child develops a secure attachment it presents as a healthy bond. Even as early as 12 months of age a child can be observed by researchers to have a secure attachment with his or her parent s or an insecure attachment.
Insecure Attachment Ψ Secure attachment a caregiver-infant relationship that provides comfort and confidence. Clingy children may grow into clingy adults. Attachment Theory Suggests That There Are Two Attachment Styles.
Basic temperament is also thought to play a partial role in attachment. Kids with insecure attachments have learned that the world is not a safe place. In other words they learn to expect the best from the other person and believe that they have a good heart.
Secure attachment can prepare a child for other social challenges and this in turn leads to their success. Insecure and secure attachment refer to specific attachment behavior patterns that the infant shows typically when being under some form of stress. While it is easiest to form a secure attachment bond with an infant attachments can be formed at any time or age.
This behavior expressed a secure attachment between Alex and his mother. These patterns have been largely shaped by the mothers sensitive responsiveness secure attachment or lack or inconsistency of responsiveness insecure attachment. Secure attachment is only one of a variety of influences such as cultural norms and individual personality differences that affect a childs process for.
Secure attachment has a lifelong effect on growth development trust and relationships. She concluded that these attachment styles were the result of early interactions with the mother. Children with insecure attachments on the other hand tend to over-react to minor stressors unable to self-regulate their stress levels.
Relating to others managing emotions. Ambivalent Avoidant Disorganized Ambivalent attachment develops when a caregiver shifts between adequate and preoccupied caregiving. Attachment is a word used by psychologists to describe the relationship between children and their caretakers who is usually their mother.
Secure attachment develops when a caregiver provides consistent caregiving. Secure attachment is characterized by trust an adaptive response to being abandoned and the belief that one is worthy of love. They expect the other person to abandon them or harm them in some way.
Infants who are securely attached have learned to trust that other people will take care of them. In people with insecure attachment however the expectation is the complete opposite. Those described as ambivalent or avoidant during childhood can become securely attached as adults while those with a secure attachment in childhood can show insecure attachment patterns in adulthood.